Big Data > Spark > b. Apache Mesos
Apache Mesos
Apache Mesos is an open-source cluster manager that functions like a kernel for a cluster of machines. It aggregates compute resources from multiple servers and allows various applications to share these resources efficiently. By acting as a resource manager across the cluster, Mesos enables better coordination and utilization of computing power.
Mesos provides APIs in Java, C++, and Python, allowing developers to request cluster resources and schedule tasks programmatically. It also includes a user-friendly web interface for monitoring and managing the cluster in real time.
One of the major advantages of Mesos is its ability to allow multiple distributed computing frameworks to run simultaneously on the same cluster. This means that both Spark and non-Spark applications—such as Hadoop, MPI, Kafka, ElasticSearch, and Apache Storm can share the same pool of nodes without interfering with each other. As a result, Mesos helps avoid redundant data copies across clusters by allowing different frameworks to process the same data in place.
Compared to Spark’s built-in Standalone cluster manager, Mesos offers a broader range of features and supports more complex use cases. It not only improves resource sharing among diverse applications but also simplifies the development of new distributed computing frameworks.
Key features of Apache Mesos include:
- Scalability to tens of thousands of nodes
- Fault tolerance for both master and slave nodes
- Multi-resource scheduling, including CPU, memory, disk, and ports
- Support for Docker containers for isolated, containerized environments
- Native task isolation to ensure secure and efficient execution
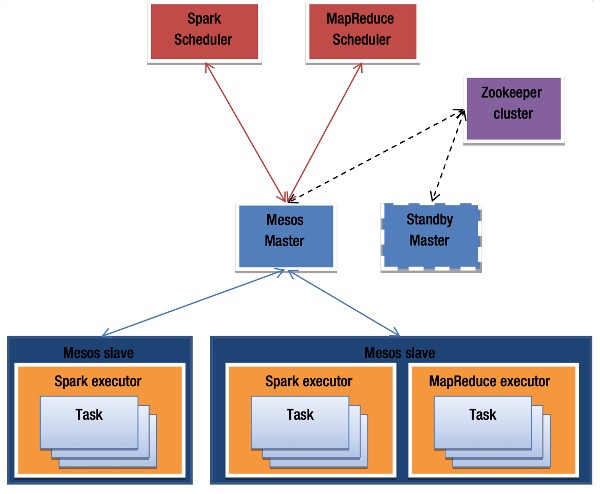
In Apache Mesos, every framework or application consists of two main components: a scheduler and executors. The executors run on the slave (worker) nodes and are responsible for executing the actual application tasks.
To ensure high availability and eliminate the risk of a single point of failure, Mesos supports multiple master nodes. At any given time, only one master is active, while the others remain in standby mode. If the active master fails, Apache ZooKeeper steps in to coordinate a seamless failover by electing a new active master.
When an application is deployed on a Mesos cluster, its scheduler connects to the Mesos master, which responds by sending a resource offer. This offer includes available compute resources (e.g., CPU cores, memory, disk space, and network ports) from the slave nodes. The amount and type of resources offered can be configured based on the needs of the application or framework.
The scheduler has the option to accept or decline a resource offer. If it accepts, the scheduler selects which specific resources it will use and sends the tasks to be executed to the Mesos master. The master then forwards these tasks to the relevant slave nodes. The slaves allocate the necessary resources to executors, which then carry out the tasks. This cycle continues—new offers are made as tasks complete and additional resources become available.
Feedback
ABOUT
Statlearner
Statlearner STUDY
Statlearner