Information Theory and Coding > Channel Capacity > What is Binary Symmetric Channel (BSC)?
Binary Symmetric Channel (BSC)
In digital communication systems the input to the channel will be the binary digits {0 , 1} and this set will also be the output alphabet. The effect of noise will not depend on the transmission pattern i.e. the channel is assumed memoryless. Ideally if there is no noise a transmitted 0 is detected by the receiver as a 0, and a transmitted 1 is detected by the receiver as a 1. However in the presence of noise, the receiver may produce a different result. In this case the information channel that arises is called a binary symmetric channel or BSC where
P(b =1 /a = 0) = P(b = 0 /a = 1)=q
This probability is called error (bit error rate (BER), or “crossover” probability.
A binary symmetric channel with crossover probability pji=P(yi/xj), is a channel with binary input and binary output and probability of error pji. That is, if X is the transmitted random variable and Y the received variable, then the channel is characterized by the conditional probabilities:
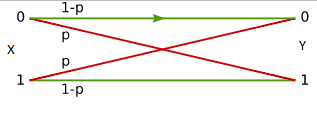
P(Y= 0/ X= 1) = P(Y= 1/ X= 0) = p,
P(Y= I/ X= 1) = P(Y= 0/ X= 0) = 1- p.
======================================
Consider a BSC with channel transition probabilities P(0/1) = p = P(1/0)
By symmetry, the capacity, max C= max I(Y;X) is achieved for p=0.5
Thus we obtained from the equation of the capacity for a BSC as
C= 1 + p log2 p + ( 1 - p) log2( 1 - p)

Entropy function H(p) =-p log2 p- (1- p) log2 (1- p)
Hence C= 1-H(p)
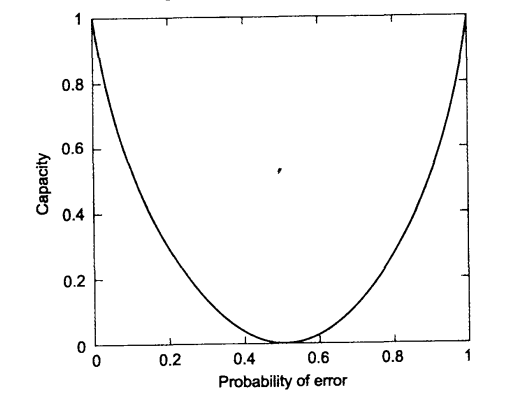
The plot of the capacity versus p is given in Figure above we can make the following observations.
- For p = 0 (i.e., noise free channel), the capacity is 1 bit/use, as expected. Each time we use the channel, we can successfully transmit 1 bit of information.
- For p = 0.5, the channel capacity is 0, i.e., observing the output gives no information about the input. It is equivalent to the case when the channel is broken.
- For 0.5 < p < 1, the capacity increases with increasing p. In this case we simply reverse the positions of 1 and 0 at the output of the BSC.
- For p = 1 the capacity is again 1 bit/use, as expected. In this case, one simply flips the bit at the output of the receiver so as to undo the effect of the channel.
Feedback
ABOUT
Statlearner
Statlearner STUDY
Statlearner