Information Theory and Coding > Entropy > Joint Entropy and Conditional Entropy
Joint Entropy and Conditional Entropy
The joint entropy H (X, Y ) of a pair of discrete random variables (X, Y ) with a joint distribution p(x, y) is defined as

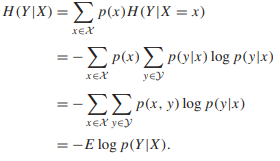
It is just the averaged over the conditioning random variable
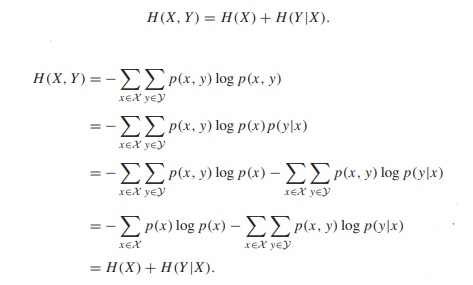
Entropy of a pair of random variables is the entropy of one plus the conditional entropy of the other.
Example: Let (X, Y ) have the following joint distribution:
|
Y X |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
Total |
|
1 |
1/8 |
1/16 |
1/32 |
1/32 |
1/4 |
|
2 |
1/16 |
1/8 |
1/32 |
1/32 |
1/4 |
|
3 |
1/16 |
1/16 |
1/16 |
1/16 |
1/4 |
|
4 |
1/4 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1/4 |
|
Total |
1/2 |
1/4 |
1/8 |
1/8 |
1 |
H(X) = - 1/2 * Log(1/2) – 1/4 * log(1/4) – 1/8 * log(1/8) - 1/8 * log(1/8) =7/4
H(Y) = - 1/4 * Log(1/4) – 1/4 * log(1/4) – 1/4 * log(1/4) - 1/4 * log(1/4) =2
H(X/Y) = 1/4 * H(X/Y=1) + 1/4 * H(X/Y=2) + 1/4 * H(X/Y=3) + 1/4 * H(X/Y=4)
= 1/4 * H( 1/8 * 4/1, 1/16 * 4/1, 1/32 * 4/1, 1/32 * 4/1 )
+ 1/4 * H(1/16 * 4/1, 1/8 * 4/1, 1/32 * 4/1, 1/32 * 4/1)
+ 1/4 * H(1/16 * 4/1, 1/16 * 4/1, 1/16 * 4/1, 1/16 * 4/1)
+ 1/4 * H(1/4 * 4/1, 0, 0, 0)
H(X/Y) = 1/4 * H( 1/2 , 1/4, 1/8, 1/8 )
+ 1/4 * H(1/4, 1/2, 1/8, 1/8)
+ 1/4 * H(1/8, 1/4, 1/4, 1/4)
+ 1/4 * H(1, 0, 0, 0)
H(X/Y) = 1/4 * 7/4 + 1/4 * 7/4 + 1/4 * 2 + 1/4 * 0 = 11/8 bits
Similarly H(Y/X) = 13/8 bits and H(X, Y) = 27/8 bits
Feedback
ABOUT
Statlearner
Statlearner STUDY
Statlearner