Machine Learning > Sampling > What is Markov process?
A Markov Chain or Markov process is a random process in which the future is independent of the past, given the present.
Consider a collection of random variables X0, X1, ….., Xn . where Xn as the state of the system at time n and suppose that the set of possible values of the Xn is the set 1, …. N . If there exists a set of numbers Pij, i, j =1,2,… N, such that whenever the process is in state i then, independent of the past states, the probability that the next state is j is Pij, the we say that the collection {Xn, n >=0} constitutes a Markov chain having transition probabilities Pij, I,j=1,2, ….N
Since the process must be in some state after it leaves state I, these transition probabilities satisfy
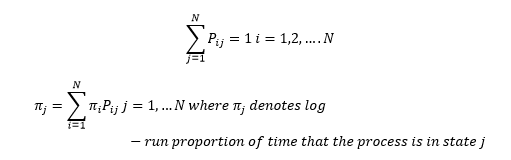
Example:
We have a restaurant that changes its menu daily. The chef is a very simple man so the only food he cooks is either fish or pasta. The choice of food he cooks can be described with the following probabilities:
P(Fish/Fish)=0.20 i.e. the probability for the chef to cook fish given the already cooked fish yesterday is 20%.
P(Fish / Pasta)=0.70
P(Pasta/Fish)=0.80
P(Pasta / Pasta)=0.30
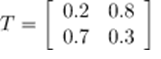
No More
What is Bayesian Analysis?
Feedback
ABOUT
Statlearner
Statlearner STUDY
Statlearner